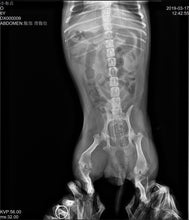
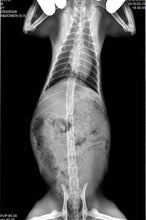
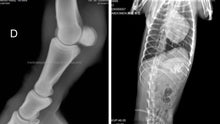
***we ship worldwide and will ship power supply for customers country on order***
***A trolley for the machine is not included with the purchase***
How many times have you finally gotten your fussy furry friend lined up with your stationary X-Ray machine, only to have them move at the last second and then have to start all over again, adding more time to your already busy schedule?
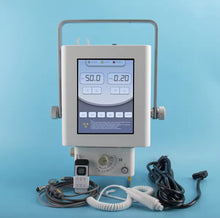
Save time and get that perfect image right the first time with the new state of the art JuvaPET Portable Digital Wireless X-Ray Machine with Flat Panel Display!
Essential Veterinary Imaging Equipment for the on the move Practitioner
Imaging platforms such as radiography and ultrasonography are frequently needed to accurately diagnose your patients’ health conditions.
Veterinary mobile imaging equipment is especially valuable to both companion animal and equine practitioners, practices that are experiencing higher demand for remote services, or practices whose limited clinic space can benefit from compact easy-to-transport equipment.
Investing in Veterinary Imaging Equipment for Your Practice
While providing exceptional patient care is always a veterinarian’s top priority, any business must stay competitive and profitable.
Having access to the newest technology in veterinary imaging equipment is an important investment in your practice’s growth and ability to deliver the following:
- A confident prognosis for your patients — Improved diagnostics lead to a confident prognosis for your patients. Veterinary imaging equipment, such as portable veterinary X-ray machines and portable ultrasound machines, provide fast, accurate, and non-invasive diagnoses, so you can promptly devise a treatment plan for your patient’s overall prognosis.
- Your ability to provide specialty care — When you have the necessary veterinary imaging equipment, you reduce the need to refer your patients to specialty providers, which allows you to stay involved with your cases, as well as retain revenue in your practice.
- Improved client satisfaction — According to the Human Animal Bond Research Institute (HABRI), the majority of pet owners consider their pet family and want the best possible care for their precious family members. They appreciate that you have state-of-the-art technology that allows diagnosis and treatment without delay and the ability to explain your findings in detail with quality imaging. Clients who have a good experience and feel their pet is receiving advanced care are more likely to be loyal to your practice and refer others to you.
- Attracting top talent — Attracting new veterinarians can be difficult in the current market. Having the latest technology in veterinary imaging is a plus in attracting talented veterinarians seeking career growth opportunities.
Stationary vs Portable Veterinary X-ray Machines
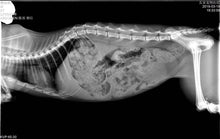
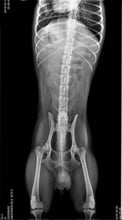
Generally speaking, a digital x-ray is primarily used to diagnose structural abnormalities such as bone malformations or fractures, as well as to detect the presence of tumors in air-filled cavities such as the lungs and some abnormalities in other organs.
Beyond the obvious benefit of being able to avoid patient transport if, for example, a pet is too ill to travel safely or a trailer ride could exacerbate a horse’s fractured limb, portable digital x-ray provides:
- Speed — Characteristic of digital x-ray in general, portable imaging units have fast processing speeds, eliminating long wait times. In addition, digital imaging technology eliminates excessive X-ray retakes, and the results are evaluated in real-time, allowing for an immediate diagnosis critical in emergency situations.
- Safety — Radiation exposure is a significant concern for patients and personnel but used appropriately, portable veterinary X-ray machines are extremely safe. Together with digital technology’s general need for fewer retakes, most systems adhere to the ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) principle of attaining high-quality imaging with the lowest dose of radiation possible.
- Image quality — This is, of course, the most important factor. Portable veterinary X-ray units are equipped with advanced technology that provides high-quality images, with many systems offering software that allows image enhancement at the workstation.
- User friendly — Portable veterinary X-ray machines are straightforward and convenient to operate. You can select the desired view from customized settings, capture an image in seconds, and save the files to the cloud or another picture archiving and communication system. Many systems provide additional software features, such as the display of measurements on the image and calculating hoof angles for equine patients.
Why choose handheld X-ray machines?
There are many benefits to using portable handheld x-ray generators and the demand is growing within the industry.
The fact that they are portable is brilliant for taking the X-ray machine anywhere, both in and out of the practice, and it provides lots of scope for field X-rays.
As they are not fixed in a designated X-ray room, there are no installation costs or building adaptations required, therefore it is a bit more economical.
They are versatile and can take images of difficult locations and angles such as dentition and distal limbs etc. Sometimes this can prove extremely challenging and sometimes even impossible with fixed machines.
In the small animal veterinary field, there is a growing use and demand for handheld radiography equipment in dentistry cases and oral radiography is evolving. In an ideal scenario, every patient undergoing a dental procedure should have dental X-rays taken before the surgery.
This will allow for a more thorough assessment of specific dental diseases such as feline oral resorptive lesions (FORL).
Key Advantages
- Plug and Play! No Special Power Needed to Operate.
- Uses Standard Wall Outlet
- Easy to Move Around Any Room to Clean or Relocate
- New Generation of Wired and Wireless DR Detectors
- Simple, Easy to Use Digital X-ray Software
- Generator and DR Can Easily Be Removed and Taken Into the Field for Equine or Bovine Applications
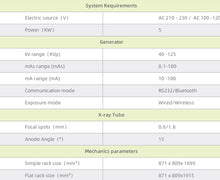
Specs:

About the Included Flat Panel Display:
How a Flat Panel Detector Works
Flat panel detectors operate through a series of systematic steps:
- X-Ray Exposure: X-rays penetrate the patient's body, with different tissues absorbing varying amounts. This leaves an X-ray "shadow" as the image contrasts which continues on to the detector.
- Conversion to Light or Charge: If the FPD is indirect, the remaining X-rays strike a scintillator material in the detector, converting them into visible light. In a direct conversion FPD, the X-rays are directly converted into an electrical charge.
- Transformation of Light to Charge: If the detector is an indirect type, the light generated in the previous step hits a layer of photodiodes, converting the light into an electrical charge.
- Generation of Image: The electric charges are then captured by a thin-film transistor (TFT) array. This array reads and amplifies the charges, translating them into a digital signal.
- Image Processing: This digital signal is sent to a computer, where it's processed into a digital image. This image is then available for viewing and diagnosis.
- Image Optimization: Finally, the image undergoes post-processing operations such as contrast adjustment, filtering, and other corrections for optimal viewing.
- Through these steps, flat panel detectors facilitate the creation of high-resolution digital images necessary for accurate medical diagnosis and patient care.
How Much Better Are Flat Panel Detectors Than Image Intensifiers?
Some significant differences between newer FPDs and older image intensifier technology make this newer equipment better and safer to use. As a result, most manufacturers are switching to FPD technology. However, which one you choose will depend on your unique radiography needs now and in the future.
One major difference is that the quality of radiographs an image intensifier produces always degrades over time. Also, its technology can create distortions in the peripheral field of view even when it’s still brand new.
FPDs, on the other hand, show minimal degradation over time, and the technology behind them is not subject to peripheral distortion. This means they’ll produce higher-quality radiographic images now and in the future.
FPDs and image intensifiers also vary significantly in their radiation dose. It concerns their use while in magnification mode since an image intensifier requires larger radiation doses to magnify the view.
On the other hand, an FPD can magnify that same view without increasing the dose, so it generally uses less radiation to produce the same or better-quality images. This makes flat panel detectors safer in the long term for both patients and the technicians or doctors working with them.
Another difference is in size. FPDs are newer technology, so it's no surprise they’re more compact than the older technology. This allows for more working space for the doctors and technicians, allowing for more precise control, especially when working with larger patients. They also have ergonomic benefits because they are easier to move around, improving functionality while relieving long-term stress on the technicians using them daily.
Cost is often an important consideration. Since flat panel detectors are new technology, they generally cost more than older technology that has been around for decades. While the initial cost savings may seem appealing if you are on an especially tight budget, it’s critical to consider the long-term costs.
Remember that image intensifiers are much more prone to degradation over time and have a much shorter lifespan.
They also generally cost more to repair. This means that you may have to repair and replace your image intensifier several times before replacing your FPD just once.
It would eliminate all those upfront savings and could make image intensifiers more expensive in the long run.
Advantages of the Flat Panel Wireless Detector:
- reliability
- wireless
- efficiency
- accuracy and informativeness
- easiness in operation
- trust and recognition from doctors around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is a Flat-Panel Detector in Radiology?
A flat-panel detector (FPD) in radiology is a device that converts X-rays into digital images. Used in various medical imaging techniques, FPDs deliver superior image quality, lower radiation doses, and faster image processing times compared to traditional film-based systems.
What Are the 2 Types of Flat Panel Detectors?
The two main types of flat panel detectors are direct and indirect conversion detectors. Direct conversion FPDs transform X-rays directly into an electric charge, while indirect conversion FPDs first convert X-rays into light and then into an electric charge. Each type has specific strengths, dictating their use in different radiography applications.
What Are Flat Panel Detectors Made Of?
Flat panel detectors are made up of several essential components:
- Scintillator Layer: Typically made of cesium iodide (CsI) or gadolinium oxysulfide (GOS), and functions to convert X-rays into other wavelengths of light.
- Photodiode Layer: Transforms the light into electric charge, often constructed from amorphous silicon.
- TFT Array: A thin-film transistor (TFT) array reads and amplifies the electric charges, and is made from materials like hydrogenated amorphous silicon.
- Glass Substrate: Provides structural integrity to the FPD.
- Electronics: Includes analog-to-digital converters, multiplexers, and other components for image processing.
- Housing: Protects the components and ensures durability, typically crafted from aluminum or plastic.
Specs: